Service
Hernia Surgery
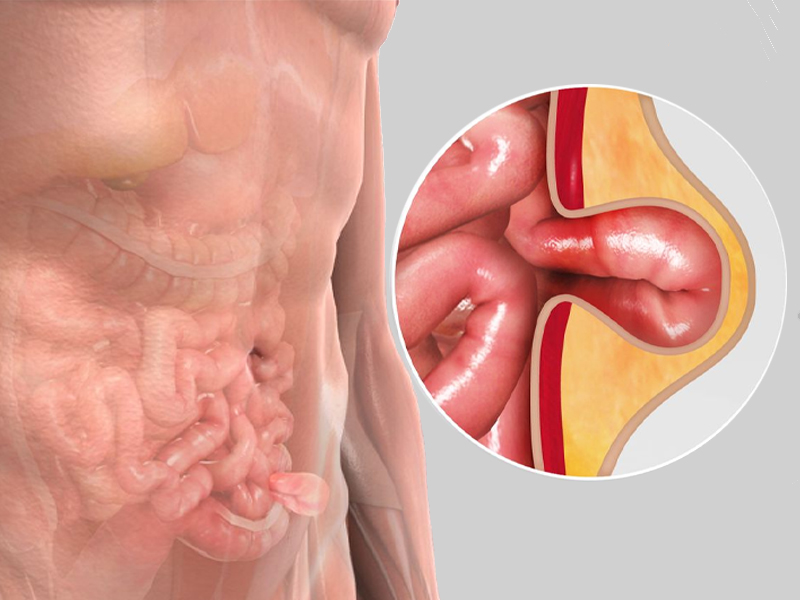
Hernia surgery is a procedure to repair a weakness in the abdominal wall that allows internal organs or tissues to bulge out. It's a common surgical procedure and is typically recommended to prevent complications like intestinal obstruction or strangulation. There are two main types of hernia repair surgery: open surgery and laparoscopic surgery, with robotic surgery being a more advanced minimally invasive option.
Types of Hernia Surgery
- Open Surgery : This involves a larger incision to access the hernia, reposition the protruding tissue, and reinforce the weakened area with stitches and sometimes a mesh.
- Laparoscopic Surgery (Minimally Invasive) : This technique uses small incisions and a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera) to guide surgical instruments. It often results in faster recovery and less pain compared to open surgery.
- Robotic Surgery : This is a more advanced minimally invasive approach where a surgeon controls robotic arms with surgical instruments, offering enhanced precision and visualization, particularly in complex cases.
Surgical Mesh
- Mesh is often used to reinforce the weakened area, providing additional support and reducing the risk of recurrence.
- Mesh materials can vary, including polypropylene, expanded polytetrafluoroethylene, and other synthetic or biological materials.
- Mesh repair can be done with both open and laparoscopic techniques.
Anesthesia
- Depending on the hernia's size and complexity, patients may receive general anesthesia (being put to sleep), regional anesthesia (numbing a specific area), or local anesthesia with sedation.
What to Expect
- The surgeon will push the bulging tissue back into the abdomen.
- The weakened area will be repaired with sutures (stitches) and possibly mesh.
- Most patients can go home the same day, but recovery time can vary.
- Light activity can usually be resumed within a few days, but heavy lifting should be avoided for several weeks.
Recovery
- Follow your surgeon's post-operative instructions carefully.
- Gradually increase your activity level as directed.
- Avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for the recommended period.
- Attend follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing.
