Service
Thyroid Surgery
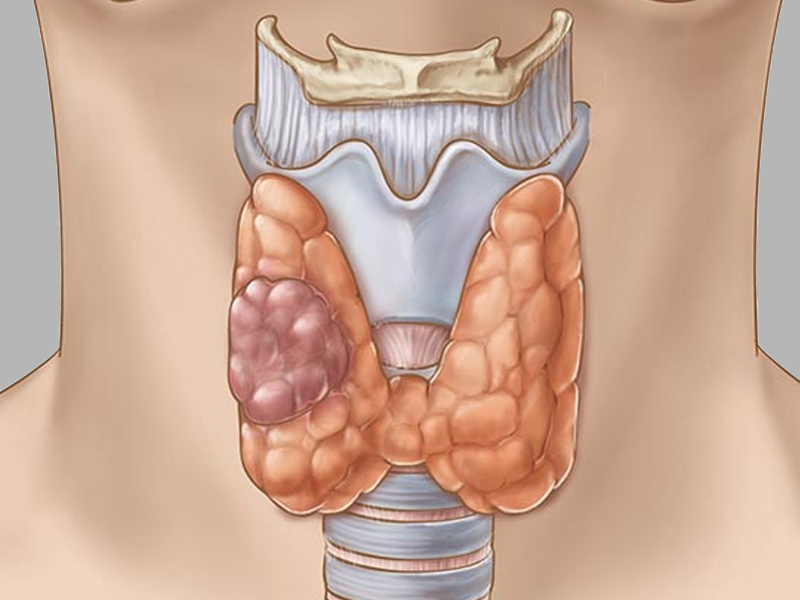
Thyroid surgery, or thyroidectomy, is a procedure to remove all or part of the thyroid gland. It's a common treatment for thyroid cancer, large goiters, and overactive thyroids (hyperthyroidism). The surgery can be a complete removal (total thyroidectomy) or a partial removal (partial thyroidectomy, hemithyroidectomy).
Reasons for Thyroid Surgery
- Thyroid Cancer : Thyroidectomy is a primary treatment for thyroid cancer, particularly for larger tumors or those with higher-risk features.
- Goiters : Enlargement of the thyroid gland (goiter) can cause breathing or swallowing difficulties, leading to surgery.
- Hyperthyroidism : When the thyroid produces too much hormone, surgery may be an option to reduce hormone levels.
- Other Conditions : Sometimes, surgery is performed for autoimmune issues, benign tumors, or excessive thyroid medication.
Types of Thyroidectomy
- Total Thyroidectomy : Removal of the entire thyroid gland.
- Partial Thyroidectomy : Removal of a portion of the thyroid gland (also known as thyroid lobectomy).
What to Expect During and After Surgery
- Procedure : Thyroidectomy is usually performed through an incision in the neck. Surgeons also identify and protect the parathyroid glands and the vocal cord nerve during the procedure.
- Recovery : Most patients can return to normal activities within a couple of weeks. Sore throat and voice changes are common initially, and some patients may experience hypothyroidism (low thyroid hormone levels) requiring hormone replacement medication.
- Complications : As with any surgery, there is a risk of bleeding, infection, and nerve damage.
Endoscopic Thyroidectomy
- Minimally Invasive : This approach uses smaller incisions and specialized instruments to remove the thyroid gland.
- Considerations : Endoscopic thyroidectomy may not be suitable for all patients, and careful selection of cases is important.
